Gerontopractitioner Training
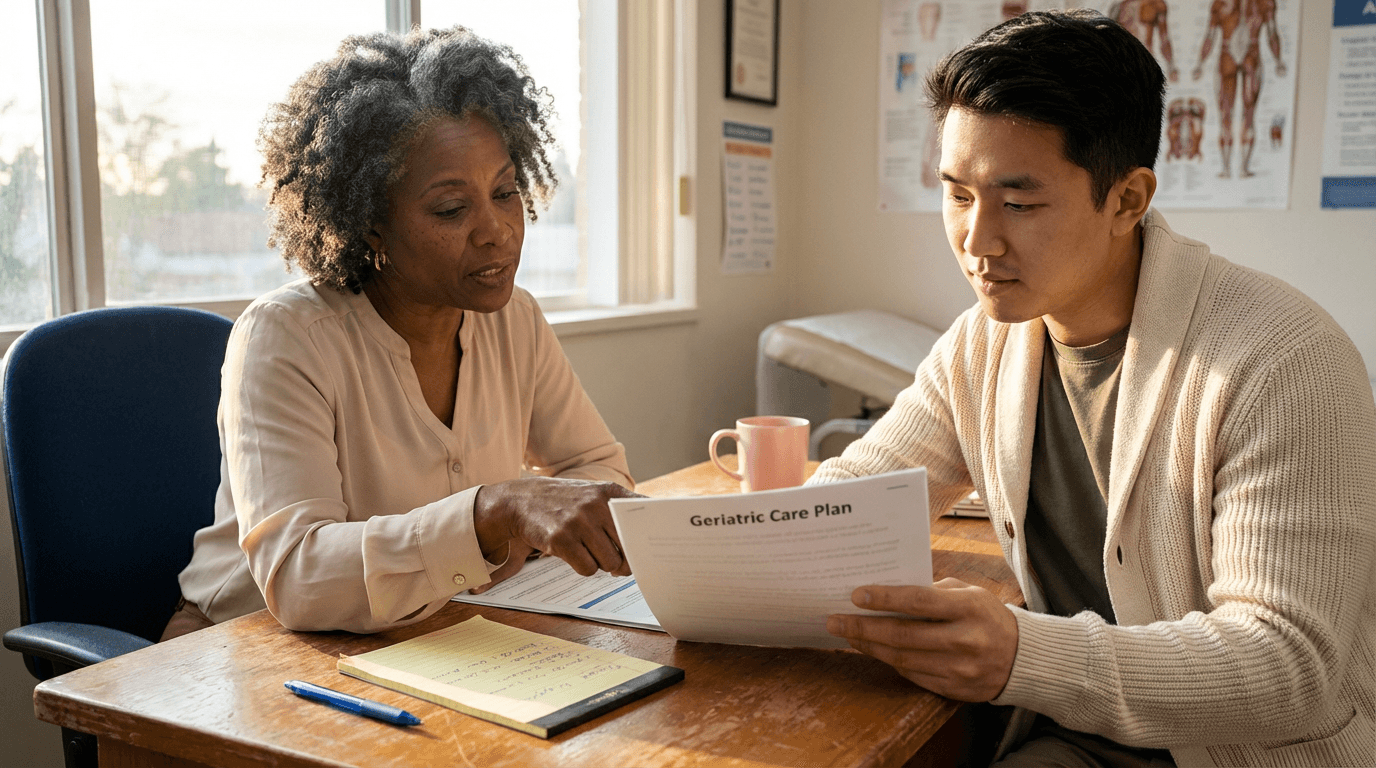
Gerontopractitioner Training provides geriatric workers with real-world methods for checking health, handling pain and falls, rehabilitation, brain and emotional care, and team care plans to boost safety, daily abilities, and life quality for seniors. It focuses on quick checks, custom plans, proven treatments for common issues like joint pain, heart failure, and sleep troubles, plus support for memory loss, feelings, isolation, and family carers in everyday settings.
from 4 to 360h flexible workload
valid certificate in your country
What will I learn?
This training equips you with hands-on, research-backed skills to evaluate pain, mood, thinking, sleep, eating habits, movement, and safety in elderly people, then create straightforward, combined care plans. You'll master drug-free and medicine-based approaches, stopping falls, planning exercises, involving families, providing social and spiritual care, recording details, and monitoring results for use right away in homes and communities.
Elevify advantages
Develop skills
- Quick elderly checks: use full geriatric tools, tests, and home risk reviews.
- Combined care plans: quickly make 3-month team plans for older patients.
- Proven elderly care: follow rules for pain, joint issues, heart failure, sleep problems.
- Movement recovery skills: create safe workouts for balance and getting around.
- Brain and social help: manage early memory loss, emotions, isolation, family carers.
Suggested summary
Before starting, you can change the chapters and the workload. Choose which chapter to start with. Add or remove chapters. Increase or decrease the course workload.What our students say
Your lessons are perfect. I got the one-year package and finally have the chance to follow several topics I'm interested in without having to switch platforms... thank you for everything you do, I've already recommended you to others...

Giulio CarloDigital Marketing Student
I like how the lessons get straight to the point and how I can switch chapters and skip content I don't need.

Mariana FerresPhotography Student
I like the content and the way the videos are presented and transcribed, which speeds up the process!

Luciana AlvarengaNail Design Student
The platform is fast and easy to use. The variety of content and the extra videos really help with learning.

Giulio CarloPrompt Engineering Student
FAQ
Who is Elevify? How does it work?
Do the courses have certificates?
Are the courses free?
What is the course workload?
What are the courses like?
How do the courses work?
What is the duration of the courses?
What is the cost or price of the courses?
What is an EAD or online course and how does it work?
PDF Course